Introduction to Probiotics and the Gut-Brain Axis
As someone who has always been interested in maintaining a healthy lifestyle, I have come across the term "probiotics" quite often. Probiotics are live microorganisms that, when consumed in adequate amounts, can have numerous health benefits. One of the most fascinating aspects of probiotics is their connection to the gut-brain axis. In this article, I will explore this connection and explain how it can impact our overall health and well-being.
Understanding the Gut-Brain Axis
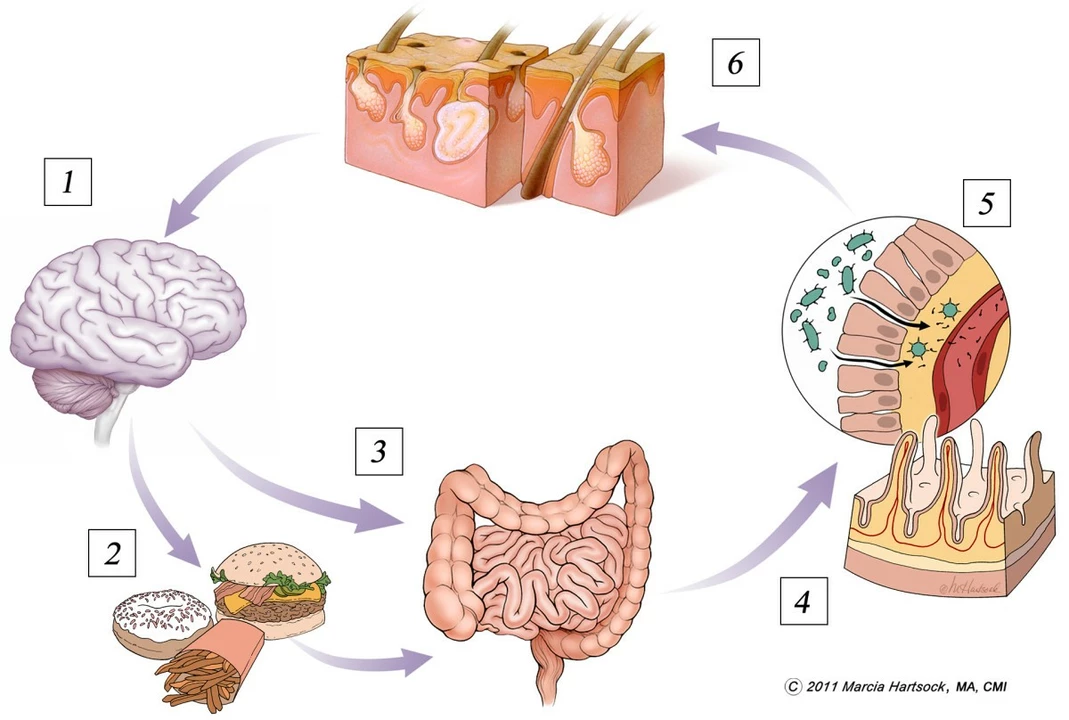
The gut-brain axis is the complex communication system between the gastrointestinal tract and the central nervous system. This communication is bidirectional, which means that messages can be sent from the gut to the brain and vice versa. The gut and brain are connected through various pathways, including the vagus nerve, the immune system, and certain hormones and neurotransmitters. This connection plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including digestion, mood, and cognitive function.
Probiotics: A Key Player in Gut-Brain Axis Communication
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can help maintain a healthy balance of gut microbiota, the community of microorganisms living in our intestines. These good bacteria can influence the gut-brain axis by producing neurotransmitters, modulating the immune system, and affecting the production of certain hormones. By doing so, they can impact our mood, cognition, and overall mental health. In this section, we will delve deeper into the ways probiotics can influence the gut-brain axis and why it's essential to maintain a healthy gut microbiota.
Neurotransmitter Production: The Bacterial Connection
Did you know that a significant portion of neurotransmitters, the chemical messengers responsible for transmitting signals in our brain, are produced in our gut? For example, about 95% of our serotonin, a neurotransmitter associated with mood regulation and happiness, is synthesized in the gastrointestinal tract. Probiotic bacteria can produce neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, which can then influence our mood and cognitive function through the gut-brain axis.
Immune System Modulation: A Key Role of Probiotics
Our immune system plays a vital role in maintaining our overall health, and it's no different when it comes to the gut-brain axis. The gut is home to a large portion of our immune system, and probiotics can help modulate its function by enhancing the production of anti-inflammatory substances and reducing the production of pro-inflammatory ones. This can impact the communication between the gut and brain, potentially reducing inflammation in the brain and improving mental health.
Hormonal Effects: How Probiotics Can Regulate Stress Responses
Another way probiotics can influence the gut-brain axis is through their effects on hormone production. For example, certain probiotic strains can help regulate the production of cortisol, a stress hormone that can have negative effects on our mental health when produced in excess. By modulating cortisol levels, probiotics may help reduce stress and anxiety and improve overall mood and well-being.
Probiotics and Mental Health: A Growing Field of Research
As the connection between probiotics and the gut-brain axis becomes more evident, researchers are increasingly interested in exploring the potential benefits of probiotics on mental health. Studies have shown that certain probiotic strains can help alleviate symptoms of depression, anxiety, and other psychological disorders. While more research is needed to fully understand the extent of these benefits, the current findings are promising and suggest that maintaining a healthy gut microbiota can have a positive impact on our mental health.
Conclusion: Prioritizing Gut Health for a Healthy Brain
Understanding the connection between probiotics and the gut-brain axis has opened up new possibilities for improving mental health through the maintenance of a healthy gut microbiota. Incorporating probiotics into our diet, whether through fermented foods or supplements, can have numerous benefits for our mood, cognition, and overall well-being. As we continue to learn more about this fascinating connection, prioritizing gut health will undoubtedly play an essential role in promoting a healthy brain and mind.
18 Comments
Landmark Apostolic Church
May 9, 2023The gut‑brain axis is a two‑way street; what we feed our microbes ends up shaping our thoughts. When the microbiota thrives, neurotransmitter production can be balanced, leading to clearer mood regulation. Conversely, dysbiosis often mirrors anxiety or cognitive fog. This dynamic reminds us that internal ecosystems are as crucial as external environments. So nurturing probiotics is not just a diet choice-it’s a strategic mental health move.
Matthew Moss
May 17, 2023It is a moral imperative that we safeguard our internal ecosystems. The neglect of probiotic intake represents a decline in personal responsibility. Consequently, we must promote disciplined consumption.
Antonio Estrada
May 26, 2023Studies have demonstrated that specific Lactobacillus strains increase peripheral serotonin levels, which can cross the blood‑brain barrier under certain conditions. Moreover, Bifidobacterium longum has been linked to reduced cortisol responses during stress tests. These findings underscore a mechanistic bridge between gut microbes and neurochemical pathways. Maintaining a diverse microbiota therefore supports both digestive and mental resilience.
Andy Jones
June 3, 2023Oh sure, because the gut just decided to write a novel on neurotransmitters for us.
Kevin Huckaby
June 11, 2023Nah, I think the hype is overblown 🤔-you can’t fix a broken brain with a spoonful of kimchi! 🌶️
Brandon McInnis
June 20, 2023Imagine a world where a simple yogurt could lift the fog of anxiety-this is the promise we’re chasing!
Aaron Miller
June 28, 2023Indeed!!! The literature-if you actually read it-shows that probiotic supplementation can modulate cortisol levels!!!
Roshin Ramakrishnan
July 6, 2023Let’s all remember!!! Different strains work for different folks!!!
Todd Peeples
July 15, 2023The psychobiotic paradigm integrates microbiota‑derived metabolites, such as short‑chain fatty acids, with neuroimmune signaling pathways 📚🧬.
Chris Smith
July 23, 2023Wow another miracle cure, because we needed that.
Leonard Greenhall
July 31, 2023A meta‑analysis of 27 double‑blind trials indicates a modest effect size (Cohen d ≈ 0.35) for anxiety reduction with multi‑strain probiotics.
Abigail Brown
August 9, 2023It’s truly inspiring to see how a tiny community of microbes can influence our emotional landscape. When you think about it, the gut is essentially a second brain, humming with chemical chatter that reaches the real brain via the vagus nerve. Probiotic research has uncovered that certain strains can boost the production of gamma‑aminobutyric acid, a major inhibitory neurotransmitter that calms neuronal firing. This means that the right bacteria might help quiet the internal storm of anxiety. Likewise, studies suggest that fermented foods can raise levels of tryptophan, the precursor to serotonin, which underpins feelings of happiness and contentment. Imagine sipping kefir and, over weeks, noticing a subtle lift in mood without a single prescription pill. Some clinicians are already recommending daily servings of yogurt as an adjunct to therapy. The synergy between diet, microbes, and mental health is becoming harder to ignore. Moreover, early trials with Lactobacillus rhamnosus have reported improved sleep quality, which in turn fuels cognitive performance during the day. Better sleep also regulates cortisol, reducing the body’s stress response. Even if the effect sizes are modest, the low risk and accessibility of probiotic foods make them a worthwhile experiment. Of course, not every strain works for every person; personal microbiome composition matters. That’s why personalized probiotic regimens are the next frontier. As we accumulate more data, we’ll be able to match strains to individual needs, much like tailoring a workout plan. Until then, incorporating a variety of fermented foods-kimchi, sauerkraut, miso-can provide a diverse microbial buffet. The collective evidence points toward a future where gut health is a cornerstone of mental wellness. Keep exploring, stay curious, and let those friendly microbes do their quiet work.
Crystal Slininger
August 17, 2023What the mainstream doesn’t tell you is that the big pharma industry is funding the gut‑brain studies to push their probiotic supplements. They quietly funnel grant money into labs that can later patent specific strains. The result? A flood of “research‑backed” products that line the shelves, while truly independent investigations get sidelined. Some whistleblowers claim that negative findings are buried under layers of corporate‑sponsored reviews. This creates a feedback loop where hype drives sales, and sales fund more hype. While there are genuine discoveries, we must stay skeptical of marketing that sounds too good to be true.
Sumeet Kumar
August 25, 2023While there’s promising data, we should stay critical and not jump on every trending kefir bottle 🧐. Randomized controlled trials are still limited, and strain‑specific effects vary. A balanced diet rich in fiber, alongside occasional fermented foods, remains a solid foundation.
Maribeth Cory
September 3, 2023Keep experimenting responsibly, and you’ll see measurable mood shifts.
andrea mascarenas
September 11, 2023Good points all around.
Vince D
September 19, 2023Great summary!
Camille Ramsey
September 25, 2023This article is totally misleadng and its claims are barely basd on real data.