Understanding Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis is a chronic and life-threatening genetic disorder that primarily affects the lungs and digestive system. In people with cystic fibrosis, a defective gene causes a thick, sticky mucus buildup that can clog the lungs, leading to life-threatening infections, and obstruct the pancreas, preventing digestive enzymes from reaching the intestines to help break down food. As a result, people with cystic fibrosis often struggle with malnutrition and poor growth, despite a healthy appetite and diet. That's why, when it comes to managing this condition, nutrition plays an essential role.
The Role of Nutrition in Managing Cystic Fibrosis
Nutrition and cystic fibrosis are intrinsically linked. The body needs a variety of nutrients to function effectively, but for individuals with cystic fibrosis, getting these nutrients can be a challenge. The thick mucus that characterizes this condition can obstruct the pancreas, preventing it from releasing enzymes that help the body absorb nutrients from food. Consequently, people with cystic fibrosis are at risk of malnutrition, which can aggravate the symptoms of the disorder. Ensuring a balanced diet is therefore crucial to promoting overall health and managing the condition.
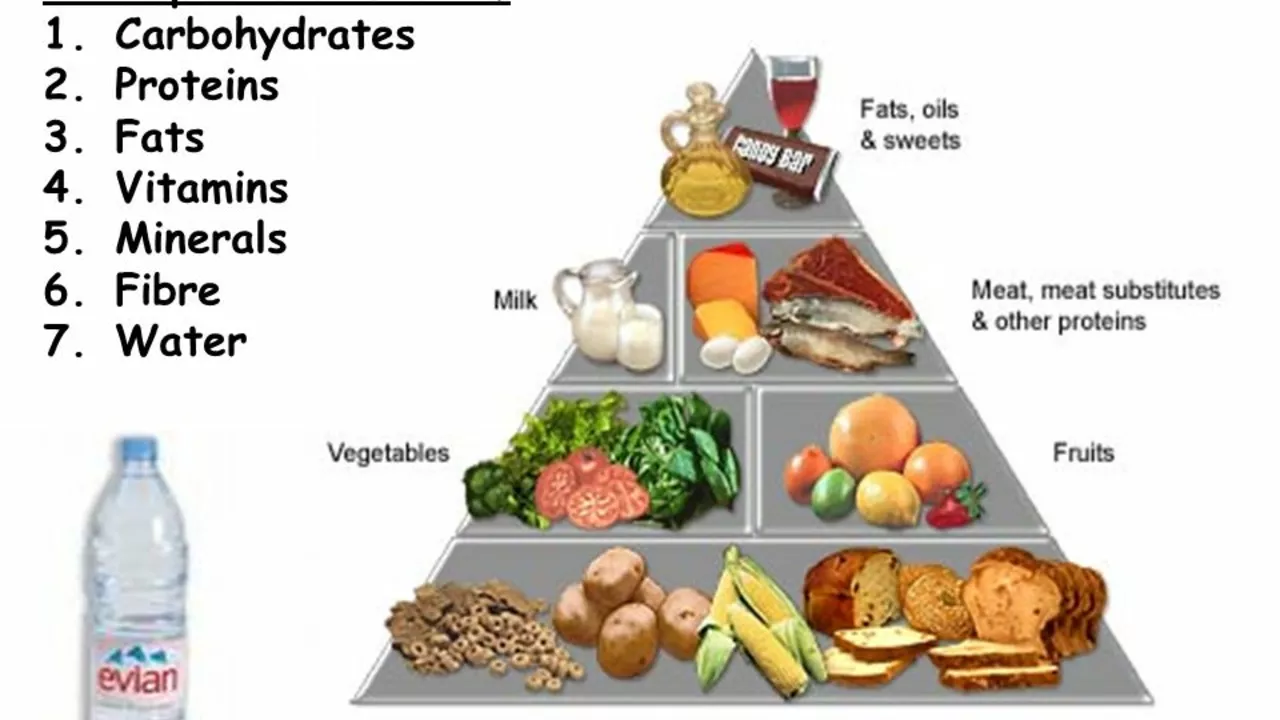
Essential Nutrients for Cystic Fibrosis
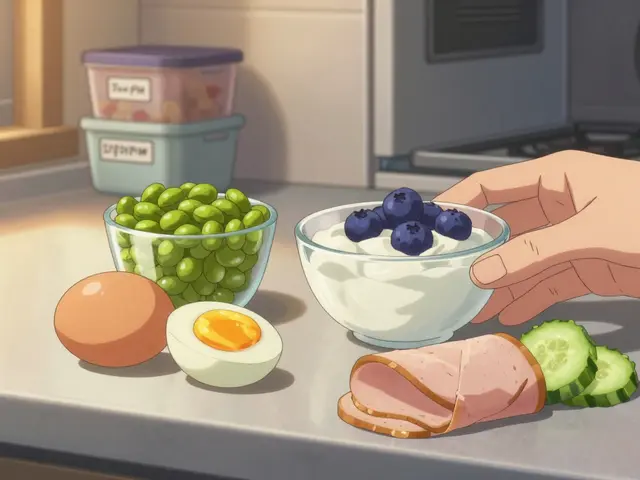
There are several nutrients that are particularly important for people with cystic fibrosis. These include high-quality proteins, healthy fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals. Each of these nutrients plays a vital role in the body, supporting everything from immune function and energy production to bone health and muscle growth. However, due to the nature of cystic fibrosis, individuals with this condition may need to consume these nutrients in larger amounts compared to those without the disorder.
High-Energy Foods for Cystic Fibrosis
People with cystic fibrosis require a high-energy diet to meet their nutritional needs. This is because the mucus in their digestive tract can make it difficult for them to absorb nutrients, meaning they need to consume more calories to compensate. High-energy foods include those rich in healthy fats, such as avocados and oily fish, as well as complex carbohydrates like whole grains and starchy vegetables. These foods provide the body with a sustained source of energy, helping to support growth and maintain overall health.
Supplementing with Vitamins and Minerals
Due to the malabsorption issues associated with cystic fibrosis, people with this condition may need to take supplements to ensure they're getting all the vitamins and minerals they need. These might include fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K, which are essential for bone health, immune function, and blood clotting. Other important nutrients include calcium, iron, and zinc. However, it's important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen, as some vitamins and minerals can interfere with certain medications.
The Importance of Hydration
Hydration is another crucial aspect of nutrition for people with cystic fibrosis. Thick mucus can lead to dehydration, which can exacerbate symptoms and make it harder for the body to absorb nutrients. Drinking plenty of water and other hydrating fluids can help to thin mucus, improve digestion, and support overall health. Additionally, hydration can help to alleviate some of the side effects of cystic fibrosis medications, such as dry mouth and throat.
Creating a Balanced Meal Plan
Creating a balanced meal plan is a key part of managing nutrition with cystic fibrosis. This involves incorporating a variety of nutrient-dense foods into each meal and ensuring adequate calorie intake throughout the day. It's also important to consider the timing of meals and snacks, as certain medications need to be taken with food. Working with a dietitian or nutritionist can be immensely helpful in putting together a meal plan that meets the unique nutritional needs of someone with cystic fibrosis.
Addressing Nutrition-Related Challenges
While maintaining a balanced diet is essential for managing cystic fibrosis, it can also present a number of challenges. These might include a lack of appetite, difficulty gaining weight, or problems with digestion. In these cases, it may be helpful to explore different strategies, such as eating smaller, more frequent meals, using nutritional supplements, or trying enzyme replacement therapy. Again, working with a healthcare provider or dietitian can be an invaluable resource in navigating these challenges.
Conclusion: The Power of Nutrition in Cystic Fibrosis
In conclusion, nutrition plays a vital role in managing cystic fibrosis. While this condition can present a number of challenges when it comes to eating and digestion, with the right strategies and support, it's possible to maintain a balanced diet that supports overall health and well-being. By prioritizing high-quality proteins, healthy fats, and a variety of vitamins and minerals, individuals with cystic fibrosis can help to manage their symptoms, promote growth, and lead healthier lives.





30 Comments
Javier Garcia
November 28, 2024This is a really interesting perspective! I've always thought that nutrition was critical for health, but I never realized just how much it impacts those with Cystic Fibrosis. What specific vitamins are usually recommended, though? I imagine that different individuals may need different supplements, right?
Also, is it common for people with CF to have to avoid certain food groups? Like, are they missing out on any typical food we usually think of as healthy? Would love to hear more about the dos and don’ts when it comes to CF diets.
christian quituisaca
November 28, 2024Absolutely, nutrition is paramount! I read somewhere that caloric intake for those with Cystic Fibrosis often doubles that of the average person. But more than calories, it’s about the quality of those calories. It's not just stuffing oneself with food; what fills their plate can really make a difference.
Anything about meal timing in relation to medication or enzyme intake? I've heard that can be crucial but then again I’m not an expert. I think having a consultant who specializes in CF nutrition is a great way to navigate this. So, yes, what’s your take on that?
Rex Wang
November 28, 2024It’s nice to see more discussions around CF and nutrition. I’m a bit of a chill observer here, but I just want to note that while a balanced diet is essential, it can be tricky! For many, adopting new eating habits can feel overwhelming, especially with the added pressure of CF.
How do people generally cope with these dietary changes? Is there a community support aspect, or is it more of an individual journey? I imagine varying personal stories could enlighten others who are just beginning this path. Would be curious to learn about how diet management looks day to day!
mark Lapardin
November 28, 2024Nutrition can be a nuanced subject, especially when coupled with medical issues like Cystic Fibrosis. There's ample jargon around the topic, but I believe the fundamentals center around being mindful of fat intake and calorie consumption.
I wonder if there are dietary guidelines or studies backing specific foods that are particularly beneficial for CF patients? An above-average calorie intake certainly sounds overwhelming...
Do you think meal plans can help streamline this effort? This could be an excellent opportunity for sharing resources about dietary education!
Barry Singleton
November 28, 2024Nutrition, eh? It leads to some toxic assumptions, if you ask me! Sure, Cystic Fibrosis patients need specific diets, but does that mean they get unfairly judged for what they eat? There’s a lot of pressure from society to maintain an ideal diet, and it rarely accounts for personal circumstances.
I'd like to hear more about how people manage not only their CF but also the societal expectations around eating. Are there community experiences in that regard? How do these individuals navigate such judgment?
Donnella Creppel
November 28, 2024Food is such a complex topic, and the importance of nutrition for those with Cystic Fibrosis can't be overstated. It's wild how necessary it is for them to consume more calories, and yet it’s not as simple as “just eat more” because of the digestive challenges they face.
Have you considered nutritional classes or workshops specific to CF patients? Those could help create a supportive environment for sharing recipes or experiences. Plus, just think: a space for people to gather and talk casually about their food adventures sounds therapeutic!
Jarod Wooden
November 28, 2024Ah, the great food debate for CF! It’s hard not to delve into philosophical territory here. One might ponder the moral dimensions of what ‘healthy’ means for CF patients. Are they obligated to follow strict nutrition guidelines irrespective of personal circumstances, tastes, or financial situations?
There’s definitely an ethical conversation around access to healthful food as well. Not everyone can afford organic or specialized diets, so, I wonder, how do we reconcile dietary suggestions with real-world limitations?
lee charlie
November 28, 2024Totally agree that nutrition is paramount for those with Cystic Fibrosis! I think hearing from CF patients about their experiences could really shed light on what works best for them. It’s one thing to read clinical recommendations, and another to hear personal stories about meals that really worked out.
Do you know of any forums or groups where patients share recipes or culinary tips? There's unity in shared experiences, and maybe we could learn a lot from their day-to-day cooking endeavors! What’s encouraged most is open dialogue around these lifestyles.
Greg DiMedio
November 28, 2024Oh boy, nutrition! Does anyone else think it’s exhausting to keep up with all of this? Like, I'm all for healthy eating, but it’s just so many rules and guidelines. For CF patients, I guess that pressure must be tenfold. Imagine trying to enjoy food while constantly monitoring caloric intake and the right nutrients. Sounds like a real drag!
Why can’t food just be food, you know? I mean, it really demystifies the joy of dining. Anyway, I hope the support is strong for these individuals navigating such tedious diets. Hang in there!
Badal Patel
November 28, 2024This topic is fascinating and could really use a dramatic lens! Cystic Fibrosis and the associated dietary needs are shadowed by hidden challenges that many might overlook when simply discussing 'healthy eating'. Nutritional aspects are intertwined with the identity of living with CF, and thus, dietary choices can feel like a constant battle!
Are there dietary heroes in the CF community advocating for unique solutions and resources? Who is leading these initiatives? Would love to discuss some of these radical changes!
KIRAN nadarla
November 28, 2024Let’s get into the complexities of this nutritional conversation! I think those with Cystic Fibrosis face not just health complications but also social dilemmas. Diets can become public topics and assumptions can spiral out of control—like, just because someone is eating differently, doesn’t mean they are unhealthy!
In fact, what if they have to avoid certain foods and feel pressured by peers? Personally, I believe strict dietary guidelines should also factor in the social aspect—how can one enjoy meals without feeling judged? Navigating through this duality can be perplexing!
Kara Guilbert
November 28, 2024Nutrition and health are crucial, especially for those dealing with conditions like Cystic Fibrosis. It grinds my gears when diet becomes a tool for judgment instead of understanding. Out there, these individuals carry the weight of both their health management and society's perception of their nutritional choices.
So, why isn't there more awareness of how diet can play a role in society’s norms? How are we supposed to create better environments for discussions when misunderstanding seems to be common? The more we talk about CF and nutrition, the closer we get to a solution!
Sonia Michelle
November 28, 2024Hey everyone! Cystic Fibrosis encompasses both a struggle for health and nutritional validation. The real question is: what’s the pathway to better understanding? Is it fostering open discussions? Maybe it's exploring diverse dietary practices and examining how they affect different people.
One engaging way to spark this dialogue is through workshops or groups focusing on recipes tailored for those with CF. Sounds like a community-building approach could really help! What else can be done to create an inclusive atmosphere where everyone feels celebrated for their choices?
Neil Collette
November 28, 2024Nutrition isn't just about fuel, it’s about creating connections! For those living with Cystic Fibrosis, balancing diet isn't merely a personal endeavor; it can also be a social experience. Food often brings people together, and yet, dietary restrictions might push individuals away from sharing that camaraderie over meals.
There's potential for a movement within the CF community—where why not have communal meals that cater to those needs? Breaking bread is often foundational in bonding, so why not orchestrate that? It’s worth considering how we can build frameworks for support!
James Lee
November 28, 2024Alright, let's talk about why nutrition for those with Cystic Fibrosis isn't just black and white. While talking about well-balanced diets sounds all nice on paper, the real struggle often lies in execution. Not everyone has access to necessary ingredients, or the means to constantly check their dietary guidelines.
This creates an elitism around health that can be, frankly, quite exhausting. Are we creating an environment that encourages guilt around certain choices? We should be shifting our focus onto promoting understanding and accessible resources instead. Just food for thought!
Javier Garcia
November 28, 2024Nutrition is indeed a critical factor in managing Cystic Fibrosis. Have you ever looked into the specific types of fats that are beneficial for those with this condition? It's interesting how certain fats can help with absorption of nutrients. You mentioned that they often need more calories, which raises a question: how do you actually go about estimating the needed calorie intake? I wonder if there are general guidelines or if it's more of a personalized approach?
christian quituisaca
November 28, 2024That's a super important angle to consider! The dietary challenges faced by those with Cystic Fibrosis are often overlooked. I recently read that protein intake is also essential—do you think it's possible that most people underappreciate its significance? Plus, I was talking to someone who has Cystic Fibrosis, and they mentioned some struggles with maintaining a healthy weight. This adds to the urgency of nutritional education in this community. It’d be awesome to create more awareness about how these dietary adjustments can really transform lives!
Rex Wang
November 28, 2024Yeah, you make a really good point. It's tough because maintaining that balance isn’t just about eating more; it's about eating right. And the idea of supplements being vital in some scenarios can't be ignored. I think it’d be useful to share personal stories or case studies on how dietary changes have directly impacted someone's health with Cystic Fibrosis. Those real-life examples might encourage others to take their nutrition seriously.
mark Lapardin
November 28, 2024Absolutely! Just to add on, being proactive with nutrition can prevent a plethora of complications down the line, especially with a chronic illness like Cystic Fibrosis. I've read that incorporating antioxidants into a diet can counteract the oxidative stress that seems prevalent in those with CF. But what should be the focus when creating a meal plan? Should it be more about calorie content, or is it essential to prioritize nutrient density as well?
Barry Singleton
November 28, 2024That's a scientific yet profound perspective! It seems like there's a nuanced route to nutrition in Cystic Fibrosis management. The balance between caloric intake and nutritional quality has a direct effect on absorption and overall health. Should we also be discussing individual tolerances to various food types? It might differ greatly from person to person, which could complicate dietary recommendations.
Donnella Creppel
November 28, 2024This whole discussion is making me realize how nuanced this topic really is! While I totally get the importance of nutrition, I sometimes feel health discourse oversimplifies things too much. It's not just about what foods are ‘good’ or ‘bad’—it’s about tailored, well-informed strategies. Plus, there’s often a socioeconomic layer that complicates food access for many individuals. Maybe we should consider those perspectives too!
Jarod Wooden
November 28, 2024You’ve hit the nail on the head there! Each patient has a unique set of needs & challenges that play into their dietary decisions. It’s fascinating to think about how lifestyle factors play into all this as well. Do you think there are certain behaviors or routines in daily life that can complement a nutritious diet? Also, how can caregivers support individuals effectively in navigating these dietary hurdles?
lee charlie
November 28, 2024Wow, what a rich conversation this has turned into! I appreciate how we’re not just skirting around the surface-level details. Nutrition seems less about restriction and more about empowerment in circumstances like Cystic Fibrosis. Balancing health while managing cravings can indeed be a tightrope walk. Has anyone explored meal prep ideas that could ease the daily burden of food choices? I’m sure that could help with stress and organization.
Greg DiMedio
November 28, 2024Ha! It’s great to see everyone be so engaged! But like, c’mon guys, is there really a magical diet for Cystic Fibrosis, or are we just throwing around concepts? People might oversimplify nutrients and their impact too much. Yes, proteins, carbs, fats—amazing! But at the end of the day, folks have to eat what they enjoy too. We should focus on finding balance, not just the science of it. What do you think?
Badal Patel
November 28, 2024This is such an intriguing post! Nutrition is indeed a fundamental cornerstone when discussing chronic conditions like Cystic Fibrosis. I once read a compelling article about how certain herbs could potentially aid digestion and absorption. Would be a game-changer if studies validated those claims! Plus, integrating holistic approaches to nutrition, alongside the scientific facts, could broaden the perspective on managing health.
KIRAN nadarla
November 28, 2024Absolutely, a multi-faceted approach makes more sense in this case! If you think of Cystic Fibrosis as a puzzle, every dietary consideration is a piece of that puzzle! Let's not forget about mental health and its ties to nutrition. Perhaps encouraging patients to enjoy their food experiences is just as important as understanding the ‘correct’ nutrients. Can we also address the emotional aspect of eating together?
Kara Guilbert
November 28, 2024Really interesting stuff here, but it does make me want to push back a little. Often the focus on nutrition seems purely clinical, and less on the lived experience of individuals battling daily challenges. Nutrition should also be enjoyable, right? I mean, eating isn’t just fuel; it’s a cultural and social experience. Wouldn’t that heavily influence a person’s dietary choices as well?
Sonia Michelle
November 28, 2024Hmmm, there's a lot to unpack here! You guys have covered many angles, but I’d like to emphasize the importance of community support. Those with Cystic Fibrosis must navigate daily dietary challenges, making having a support network so crucial. Whether it’s family or friends, how do you see others being instrumental in this process? Can regular meetups around food create an encouraging environment?
Neil Collette
November 28, 2024Looks like we're all a bit passionate about this! But then again, can we take a sec to acknowledge the barriers? Accessibility to quality foods, living with a chronic illness, and the cost of supplements can really hamper dietary advancements. How can we educate on navigating these barriers while still promoting a healthier lifestyle for these individuals? It’s all interlinked, really.
James Lee
November 28, 2024It’s an open-ended question, but I think many are missing the simplicity of it all. Life is too short not to enjoy what you eat! While I recognize the importance of nutrition in managing illnesses, how can we convey that eating well doesn’t mean sacrificing taste? It may seem trivial, but what about flavor? Combining tasty meals with necessary nutritional values could be the sweet spot. Any thoughts on that?